Energy Test Review Sheet
Enzymes
Enzyme Notes
Enzyme Structure and Function - their job
-
What type of macromolecule is an enzyme? (carbohydrate, protein, lipid, nucleic acid)
- Protein
-
What is the job of an enzyme?
- Speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy required for biochemical reactions.
-
Activation Energy, Substrate, Active Site
- How do enzymes work? How do they make reactions happen so quickly?
- Enzymes work by binding to substrates at the active site, temporarily forming an enzyme-substrate complex that reduces the activation energy needed for the reaction, thereby speeding it up.
- How do enzymes work? How do they make reactions happen so quickly?
-
Draw and label an enzyme with a substrate, reactants, and products. Use the potato experiment and hydrogen peroxide and catalase as your example:
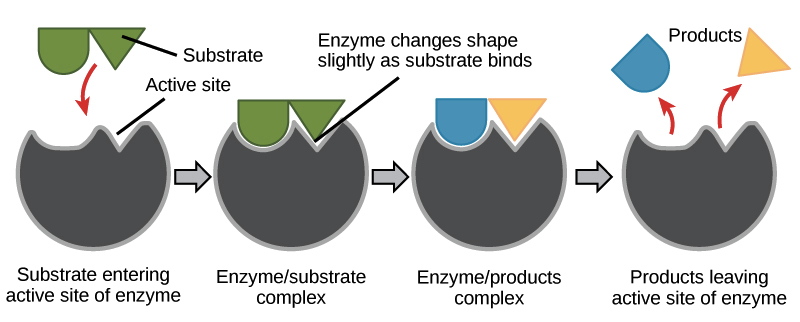
-
Factors affecting enzymes, denaturation
- Name 4 factors that affect the rate of an enzyme:
- a. Temperature
- b. pH level
- c. Salt level
- d. Concentration
- Name 4 factors that affect the rate of an enzyme:
-
What happens if an enzyme is in an extreme environment?
- Denatures
-
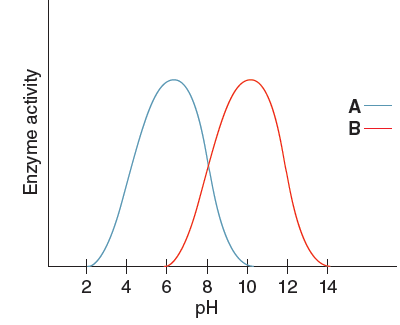
Explain the graph of pH and enzyme activity above:
- Every enzyme has its own ideal level of pH. When the pH is at the optimum level, the enzyme will act at a faster rate.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Notes
Formula for Photosynthesis
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + sunlight → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Light Dependent and Light Independent Reactions
- Light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes and produce ATP and NADPH.
- Light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle) occur in the stroma and use ATP and NADPH to synthesize glucose. d. How can photosynthesis be measured?
- By oxygen output, glucose production, or CO₂ uptake.
Photosynthesis Details
- Step: Light Reaction
- Where it happens: Thylakoid membrane
- Requires: Sunlight & Water, ADP, NADP⁺
- Produces: ATP, NADPH, O₂
- Step: Calvin Cycle (Light Independent Reaction)
- Where it happens: Stroma
- Requires: CO₂, ATP, NADPH
- Produces: Glucose
Chloroplast Structure

Molecules in Photosynthesis
- ATP & ADP cycle
- ADP -> ATP (ADP is not charged, ATP is charged with energy)
- NADP⁺ -> NADPH (NADP⁺ is not charged, NADPH is charged with hydrogen ions and electrons)
| Step | Where It Happens | Requires | Produces |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Reaction | Thylakoid Membrane | Sunlight & Water, 2 ADP, 2 NADP+ | ATP, NADPH, O2 |
| Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reaction) | Stroma | 6 CO2, 18 ATP, 12 NADPH | Glucose, 18 ADP, 12 NADP+ |
Cell Respiration & Fermentation
Cell Respiration Notes
Where Cell Respiration happens
- In the mitochondria.
When does fermentation occur?
- When no oxygen is available for aerobic respiration.
Cell Respiration Details
-
Step: Glycolysis
- Where: Cytoplasm
- Requires: Glucose
- Produces: 2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
-
Step: Krebs Cycle
- Where: Mitochondrial Matrix
- Requires: 2 Acetyl CoA
- Produces: 6 CO₂, 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH₂
-
Step: Electron Transport Chain
- Where: Inner mitochondrial membrane
- Requires: O₂, NADH, FADH₂
- Produces: H₂O, approximately 32-34 ATP
Molecules in Cell Respiration
-
NAD⁺/NADH cycle
- NAD⁺ is not charged, while NADH is charged with electrons and hydrogen ions.
-
FAD/FADH₂ cycle
- FAD is not charged, while FADH₂ is charged with electrons and hydrogen ions.
| Step | Where | Requires | Produces |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycolysis | Cytoplasm | Glucose, 2 ADP, 2 NAD+ | 2 Pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH |
| Krebs Cycle | Mitochondrial Matrix | 2 Acetyl CoA, 2 ADP, 2 FAD | 6 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2 |
| Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis | Mitochondrial Inner Membrane | O2, 8 NADH, 2 FADH2 | H2O, 32 ATP (Theoretically up to 34 ATP) |
Fermentation Types
- Lactic Acid Fermentation
- Occurs in muscle cells and some bacteria and yeast without oxygen.
- Glucose is required and produces lactic acid and 2 ATP.
- Alcoholic Fermentation
- Occurs in yeast and some bacteria without oxygen.
- Glucose is required and produces ethanol and 2 ATP.
| Type | Where | Requires | Produces |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactic Acid Fermentation | Muscle cells, bacteria, yeast | Glucose, 2 ADP, 2 NAD+ | Pyruvate, Lactic acid, 2 ATP, 2 NADH |
| Alcoholic Fermentation | Yeast | Glucose, 2 ADP, 2 NAD+ | Pyruvate, Ethanol, CO2, 2 ATP, 2 NADH |